
With the latest JDK installed, you can now develop and run Java applications on your system. You have successfully installed Java 20 on Fedora and CentOS Steam 9/8 and RHEL 9/8. Set the Java environment variables using the following commandsĮxport PATH=$PATH:/usr/java/jdk-20.0.1/binĪlso, put all the above environment variables in /etc/environment file for auto-loading on system boot. Most Java-based applications use environment variables to work. Step 4 – Setup Java Environment Variables Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 20.0.1+11, mixed mode, sharing) Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 20.0.1+11) The alternatives binary is provided by chkconfig package. But in case the system is still using the older version, use alternatives command to change the default Java version. Once the installation is completed, this version will be the default Java version.
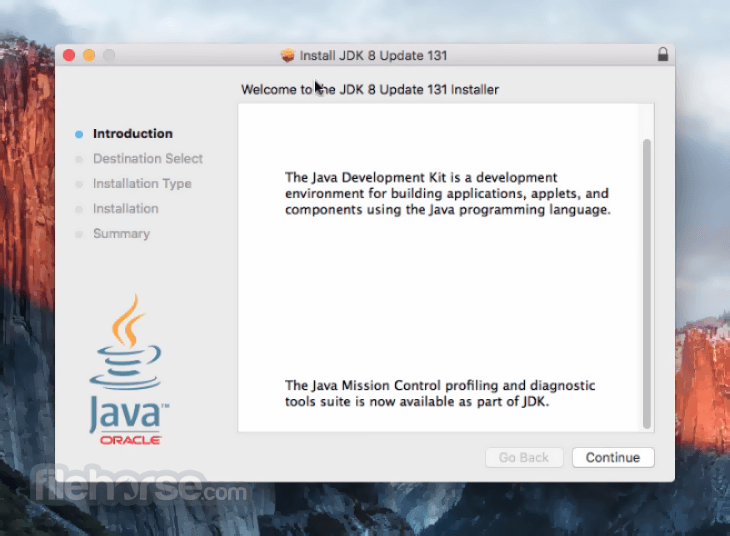
The non-root user must use `sudo` run command with special privileges that allow the installation.Įxecute the following command to install Java 20: sudo rpm -Uvh jdk-20_linux-圆4_bin.rpm Alternatively, you can use the command-line tool ‘wget’ to download the file directly: wget Step 3: Installing Java 20Īfter downloading the Java package file, use the `rpm` command to install it on your system. Select the appropriate version for your system (Linux 圆4 Compressed Archive). Navigate to the official Oracle JDK website ( ) to download the latest JDK 20 release. To do this, run the following commands: sudo dnf update -y Step 2: Download Java 20
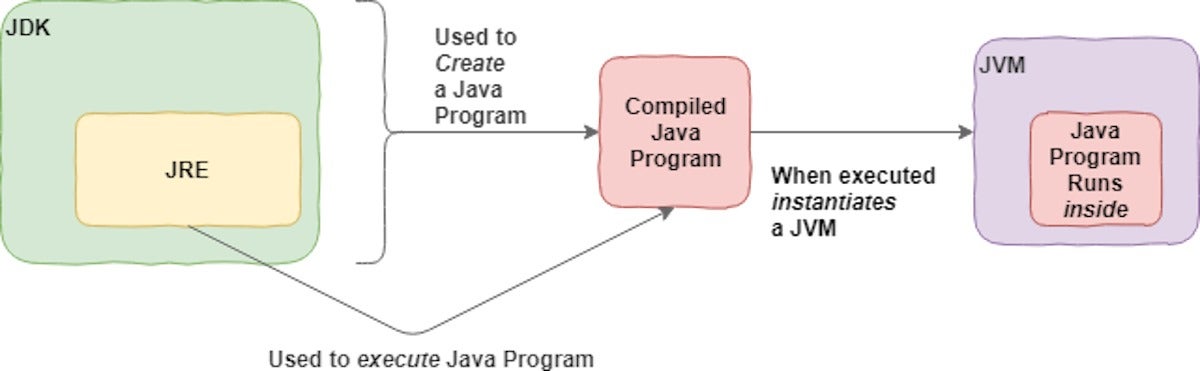

Java 20 is a non-LTS version that introduces numerous enhancements and features, showcasing the future direction of the language and its ecosystem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
